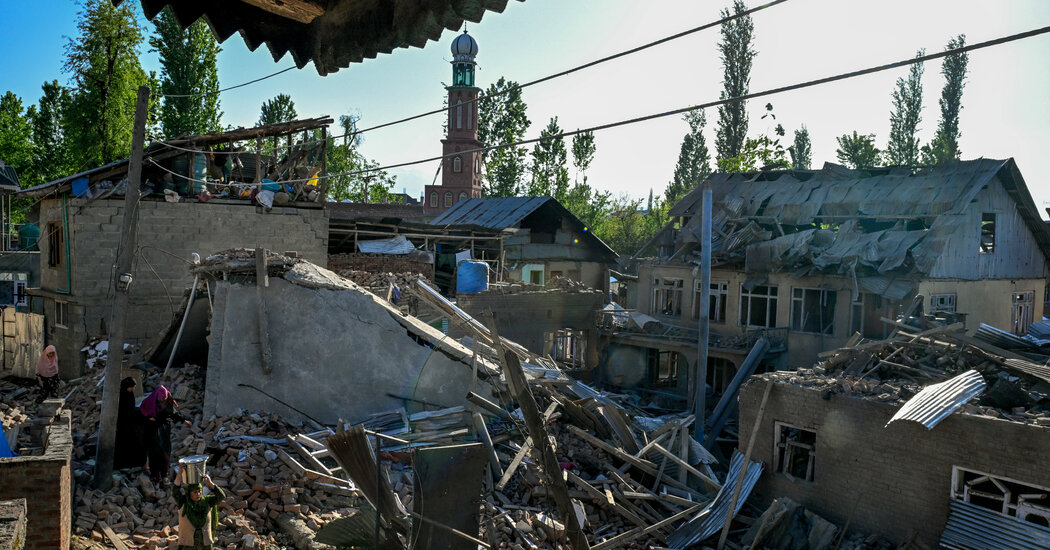
As investigators pore over the chain of events that plunged large swathes of Spain, Portugal and parts of southern France into darkness earlier this week, a prominent figure in the Bitcoin mining sector has argued that the catastrophe was “highly unlikely” to have unfolded had the Iberian grid been equipped with large-scale, fast-acting mining operations.
Daniel Batten, an advisory-board member of Marathon Digital Holdings (NASDAQ: MARA) and co-founder of climate-technology investor CH4 Capital, used X to critique what he called the “partial” nature of Europe’s renewable-energy transition. Batten posted a real-time generation snapshot taken at 12:30 p.m. local time, just five minutes before the cascading failure, showing the grid “running with very little … dispatchable spinning generation,” the rotating mass of thermal or nuclear turbines that traditionally provides inertia and frequency stability.
Bitcoin Mining May Hold The Key
“Would large-scale Bitcoin mining deployment have prevented the power outages in Spain/Portugal?” he asked. “Short answer: ‘Yes.’” Batten contends that, in the absence of inertia from conventional plants, “renewables don’t [provide it], making the grid more fragile if you don’t have a way to very rapidly load-balance in the case of an outage.”
Bitcoin miners, he argues, supply precisely that controllable load. In Texas, whose ERCOT system recorded wind-and-solar penetration of 76% on one spring day, grid operators can curtail roughly 3 GW of mining demand in “under a second.” That capability, Batten wrote, “consistently and instantly balance[s] frequency in lieu of spinning reserve,” allowing ERCOT to ride through sudden supply-demand mismatches that would otherwise trigger the same automatic protections that collapsed the Iberian grid.
“What happened in Spain and Portugal is not an inherent risk of renewables,” Batten continued. “It’s what happens when the renewable-energy transition is done in a partial way, without due consideration to load balancing … We have the solutions right under our noses, let’s start using them.”
Batten’s post drew immediate push-back from some. X user Aurum Digitalis replied that “the longer short answer is: We don’t know. But it would have helped the grid by acting like a flexible load.” Batten accepted the epistemic caution while maintaining his thesis: “Correct, the only way you can know something with certainty is if it happens. Equally, there is good evidence to say it’s highly unlikely the event would still have happened … given that the root cause … was lack of spinning reserve at the time.”
Spanish and Portuguese authorities have so far attributed the blackout to a “significant power imbalance” that triggered automatic shutdowns designed to protect critical equipment. They have ruled out cyber-intrusion and are focusing on a technical failure somewhere in the synchronous Iberian Peninsula grid. Full service was restored overnight, but the incident has reignited debate over how quickly dispatchable backup and advanced demand response must scale as Europe approaches its 2030 renewable-energy targets.
Batten insists that Bitcoin mining should be part of that toolkit, alongside batteries. He notes that mining infrastructure is “modular and low-cost to deploy” and can reduce retail tariffs by absorbing excess generation that would otherwise be curtailed at the grid operator’s expense. Batteries, he adds, “are part of the solution too,” but serve a different niche because they deliver energy, whereas miners primarily absorb it on cue.
At press time, BTC traded at $94,503.

Featured image created with DALL.E, chart from TradingView.com

Editorial Process for bitcoinist is centered on delivering thoroughly researched, accurate, and unbiased content. We uphold strict sourcing standards, and each page undergoes diligent review by our team of top technology experts and seasoned editors. This process ensures the integrity, relevance, and value of our content for our readers.