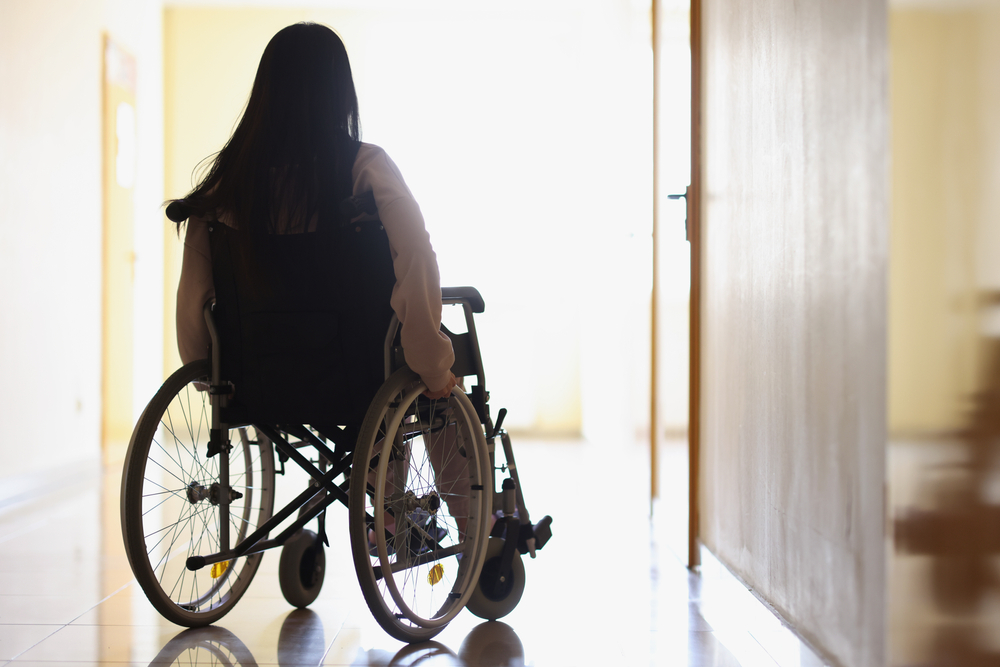
With the evolution of Egypt’s infrastructure, the need for an inclusive infrastructure that caters to persons with disabilities (PWDs) has never been more pressing due to the statistics provided.
With approximately 12 million individuals living with disabilities in the country, representing about 35 percent of the population when considering their families, the urgency to create accessible environments is paramount.
As a result, the Egyptian government has made significant strides in recent years, particularly with the establishment of the National Council for Persons with Disabilities and the Differently Abled Fund, which aim to empower PWDs and ensure their rights are upheld.
However, the challenge remains: how can Egypt effectively integrate these initiatives into its infrastructure to create a truly inclusive society?
Public transportation for PWDs
Public transportation plays a pivotal role in the daily lives of millions of Egyptians. Its significance is derived from being a key cornerstone of the state’s infrastructure and a principal socio-economic element of Egypt’s pathway towards achieving the 2030 agenda of inclusivity and social development.
Accordingly, the Egyptian government has invested around EGP 1 trillion (USD 19 billion) toward its new urban development plans that aim to link various parts of Greater Cairo to enable easier commuting to the New Administrative Capital.
In this context, ensuring a socially inclusive transportation network for citizens, including PWDs, represents a significant challenge for the government as well as an economic necessity, especially in light of the removal of fuel subsidies.
Accessibility, in this context, refers to the degree of usability and availability of transportation services for PWDs. It encompasses assistive technology, inclusivity, social security, and the ability to navigate smoothly from one point to another.
The constitutional and legal frameworks established in recent years, including the 2014 Constitution and Law No. 10 of 2018, provide a solid foundation for the rights of PWDs. These laws emphasize accessibility and integration, mandating that public facilities be adapted to meet the needs of all citizens.
Yet, despite these advancements, many barriers persist. Public transportation systems still lack the necessary adaptations, such as ramps and elevators, which are crucial for wheelchair users.
In recent years, the Egyptian government has turned its attention to supporting PWDs comprehensively, announcing 2018 as the year of persons with disabilities. This coincided with the launch of Law No. 10/2018, which represents guidelines for the government’s subsequent efforts on the matter.
A significant component of the law is its alignment with the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, ensuring non-discrimination and equality in all human rights and personal freedoms.
The Ministry of Social Solidarity has also launched integrated smart cards to facilitate access to services intended for PWDs, enabling discounts on transportation and other governmental transactions.
Socio-economic policies have been introduced to support PWDs in the transportation sector, including discounts on public transportation tickets and the introduction of integrated smart cards.
Infrastructural development policies focus on assistive technology and usability, with the government working on an accessibility code to enable PWDs to use transport vehicles and stations effectively. Recent collaborations between the Ministry of Transport and the Ministry of Social Solidarity aim to ensure accessible public transportation services in line with this code.
Learning from other countries, such as South Africa, which has developed comprehensive databases to integrate PWDs’ needs into public transportation policies, Egypt can adopt similar strategies to enhance accessibility.
By learning from such models, Egypt can improve its own infrastructure and policies, ensuring that people with disabilities have the support needed to engage in various aspects of society, including tourism as well.
The Role of Inclusive Tourism in Empowering People with Disabilities
One of the most crucial social impacts of accessible tourism is that it empowers local people with disabilities to engage more actively in society. By providing accessible tourism facilities, people with disabilities can fully participate in tourism activities, contributing to their inclusion in broader societal activities.
This inclusive approach to tourism can also drive demand from tourists in developed countries where accessible tourism is highly sought after.
Furthermore, accessible tourism can encourage domestic travel, as people with disabilities often prefer to travel with family or friends to nearby destinations accessible by various transportation methods.
Travel agencies can benefit significantly from providing services to disabled tourists, as these efforts can improve service quality, increase economic sustainability, reduce seasonality, make businesses more competitive, and open new market opportunities.
As illustrated in the research, offering services tailored to people with disabilities can be beneficial for the tourism sector as a whole.
By prioritizing accessibility in its urban planning, tourism, and transportation strategies, the nation can enhance the quality of life for PWDs.